







 |
 |

| 年龄 Age |
人数 Person |
周 Weeks |
平均 Average |
最少 Min |
最多 Max |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
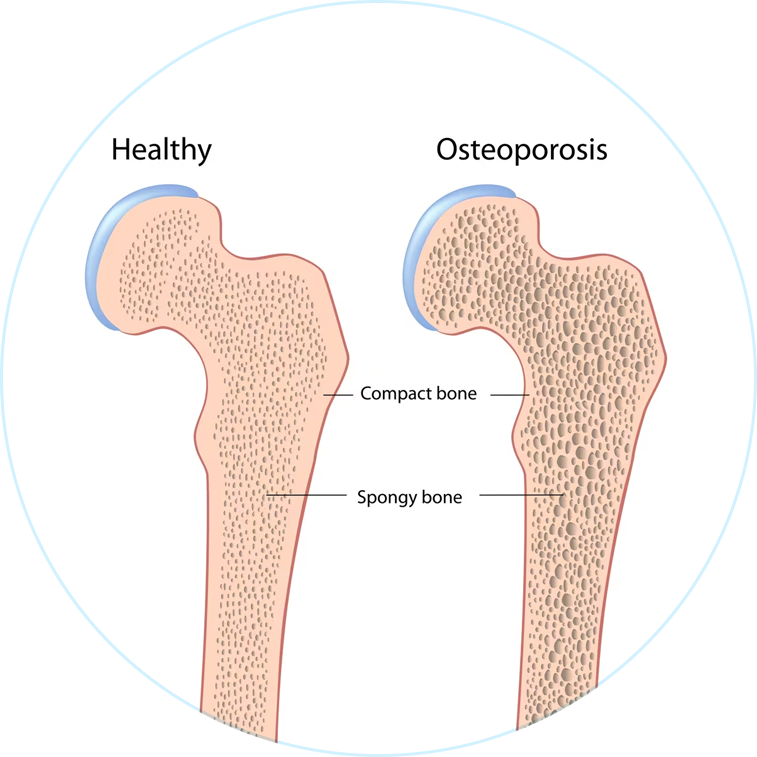
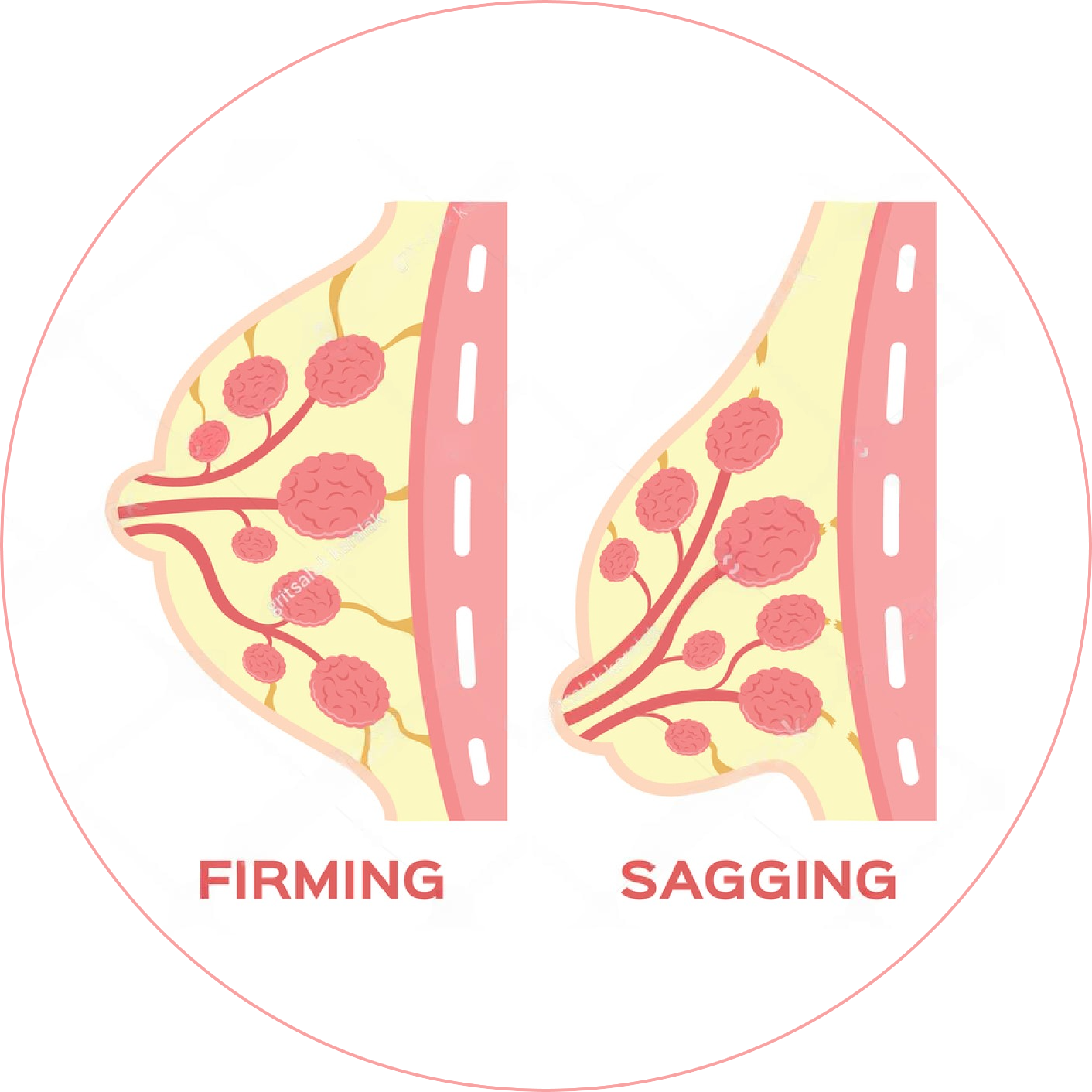
| 皮肤弹性 Skin Elasticity |
35–65 | 114 | 8 | +10% | +6% | +51% |
| 皮肤水分Skin Hydration | 35–55 | 66 | 8 | +26% | +18% | +29% |
| 皱纹体积减少 Wrinkle Reduction |
35–65 | 114 | 8 | –25% | -9% | -51% |
| 胶原 I 含量 Procollagen I ↑ |
45–65 | 10 | 8 | +65% | ||
| 弹性蛋白含量 Elastin ↑ |
45–65 | 10 | 8 | +18% | ||
| 橘皮组织 Cellulite |
24–50 | 105 | 24 | -9% | -5% | |
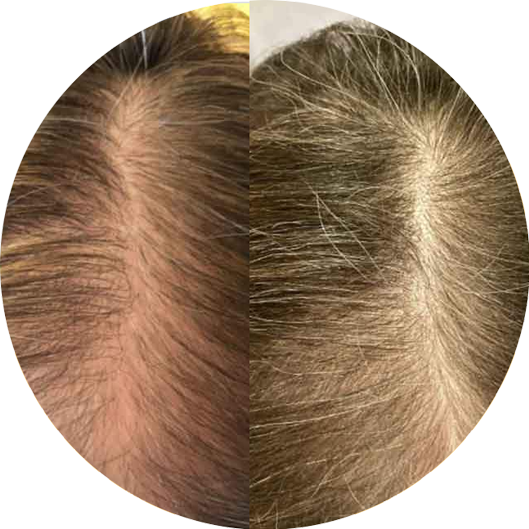
| 头发 Hair | 39-75 | 44 | 16 | +1.93µm | ||
| 实验项目 | 研究名称(作者) | 链接 |
|---|---|---|
| 弹性、水分、皱纹 Elasticity, moisture, wrinkles |
Proksch, E., Zdzieblik, D., & Oesser, S. (2025). – The Oral Intake of Specific Bovine-Derived Bioactive Collagen Peptides Has a Stimulatory Effect on Dermal Matrix Synthesis and Improves Various Clinical Skin Parameters | MDPI |
| 弹性、水分、皱纹 Elasticity, moisture, wrinkles |
Proksch et al., 2014 – Oral intake of specific bioactive collagen peptides reduces skin wrinkles and increases dermal matrix synthesis | PubMed 24401291 |
| 皮肤活检(胶原/弹性蛋白) Skin biopsy (collagen/elastin) |
Proksch et al., 2014 – Oral supplementation of specific collagen peptides has beneficial effects on human skin physiology: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study | PubMed 23949208 |
| 橘皮组织改善 & 真皮密度 Cellulite Improvement & Dermal Density |
Schunck et al., 2015 – Dietary Supplementation with Specific Collagen Peptides Has a Body Mass Index-Dependent Beneficial Effect on Cellulite Morphology | PubMed 26561784 |
| 头发 Hair |
The oral intake of specific Bioactive Collagen Peptides has a positive effect on hair thickness | Gelita Publication |

| 多重信号肽 - 进入成纤维细胞,激活 TGF-β/SMAD 路径,刺激胶原合成 Multiple signaling peptides – enter fibroblasts, activate the TGF-β/SMAD pathway, and stimulate collagen synthesis. |
| 抑制 MMP 表达或活性(MMP-1又叫胶原酶1,会直接分解I型和III型胶原蛋白) Inhibit MMP expression or activity (MMP-1, also known as collagenase-1, directly breaks down type I and type III collagen). |
| 激活免疫信号、抗氧化通路、减少促炎细胞因子 Activate immune signaling, antioxidant pathways, reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines |
| 胶原生成 | 促进成纤维细胞合成 I型、III型胶原蛋白 |
| Collagen synthesis | Promote fibroblasts to synthesize type I and type III collagen. |
| 皮肤修复 | 加快伤口愈合,重建真皮结构 |
| Skin regeneration | Accelerates wound healing and restores dermal structure. |
| 抑制炎症 | 控制免疫反应,防止伤口过度发炎 |
| Reduce inflammation | Regulate immune responses and prevent inflammation in the body. |
| 调节细胞增殖 | 控制成纤维细胞、角质形成细胞的活性与分裂 |
| Control cell growth | Control the activity and proliferation of fibroblasts and keratinocytes. |
| 诱导 ECM | 增加透明质酸与弹力蛋白,维持皮肤支撑力与含水量 |
| Induce ECM (extracellular matrix) | Increase hyaluronic acid and elastin to maintain skin support and hydration. |






| 千年前 | 人们通过长时间炖煮动物骨头、皮、蹄(如鱼鳞、猪皮、牛骨)制成高汤、肉冻,天然富含胶原蛋白。 |
| 中世纪 | 宫廷甜品与胶冻 |
| 19世纪 | 法国、英国开始工业化生产明胶,主要用于食品增稠剂、糖果(如棉花糖、QQ糖)、果冻等。 |
| 20世纪中后期 | 科学家发现普通明胶分子大、吸收差,开始研发水解胶原蛋白肽(更易吸收)。 |
| 21世纪 | 大量研究显示:特定小分子胶原肽可改善皮肤弹性、含水量、关节健康。 |